有的没的
有蛮长时间没更新了,笔记一直有在做,不过暂时都放在本地了,因为有些还不太完整(选定的每篇范围太大也是一个原因)。加上最近在实习,大部分笔记放在内部的笔记软件中。不过因为Sentinel有很大一部分是开源的,所以将笔记中有关开源的分析部分重新整理出来公开了,这段时间应该陆续会有笔记被放到这边。 文中没标注的部分资料(图片)来源于文末参考链接。
经典限流算法
计数器算法
Sentinel 中默认实现的 QPS 限流算法和 THREADS 限流算法都属于计数器算法。QPS 限流的默认算法是通过判断当前时间窗口(1 秒)的 pass(被放行的请求数量)指标数据判断,如果 pass 总数已经大于等于限流的 QPS 阈值,则直接拒绝当前请求,每通过一个请求当前时间窗口的 pass 指标计数加 1。THREADS 限流的实现是通过判断当前资源并行占用的线程数是否已经达到阈值,是则直接拒绝当前请求,每通过一个请求 THREADS 计数加 1,每完成一个请求 THREADS 计数减 1。
漏桶算法(Leaky Bucket)
漏桶就像在一个桶的底部开一个洞,不控制水放入桶的速度,而通过底部漏洞的大小控制水流失的速度,当水放入桶的速率小于或等于水通过底部漏洞流出的速率时,桶中没有剩余的水,而当水放入桶的速率大于漏洞流出的速率时,水就会逐渐在桶中积累,当桶装满水时,若再向桶中放入水,则放入的水就会溢出。我们把水换成请求,往桶里放入请求的速率就是接收请求的速率,而水流失就是请求通过,水溢出就是请求被拒绝。
令牌桶算法(Token Bucket)
令牌桶不存放请求,而是存放为请求生成的令牌(Token),只有拿到令牌的请求才能通过。原理就是以固定速率往桶里放入令牌,每当有请求过来时,都尝试从桶中获取令牌,如果能拿到令牌请求就能通过。当桶放满令牌时,多余的令牌就会被丢弃,而当桶中的令牌被用完时,请求拿不到令牌就无法通过。
数据模型
核心类
ArrayMetric
Metric的实现类,数据节点的addRtAndSuccess最后会落到该类上,该类也是sentinel记录数据模型的最外层包装
内部持有一个LeapArray<MetricBucket> data数据结构作为对窗口的包装,所有操作都会落到该数据结构上
构造方法通过传入参数的差异,为data赋值不同子类的引用(秒级窗口OccupiableBucketLeapArray,分钟级窗口BucketLeapArray)
LeapArray
内部持有一个AtomicReferenceArray<WindowWrap<T>>的数据结构作为实际容纳窗口的容器,各种操作会在该类中获取对应的WindowWrap<T>再进行相关操作
成员变量
protected int windowLengthInMs;
每个窗口长度(Ms)
protected int sampleCount;
滑动窗口内样本个数
protected int intervalInMs;
LeapArray总时间(Ms)
private double intervalInSecond;
LeapArray总时间(s)
protected final AtomicReferenceArray<WindowWrap
private final ReentrantLock updateLock = new ReentrantLock();
更新WindowWrap<T>的锁
WindowWrap
窗口包装类,主要用于包装MetricBucket,记录窗口元信息
成员变量
private final long windowLengthInMs;
窗口长度
private long windowStart;
窗口开始时间
private T value;
被包装的类
MetricBucket
实际数据存放类
维护了一个LongAdder数组counters,用于记录各种数据,包括以下几种
1 | public enum MetricEvent { |
核心方法
获取数据(以success为例)
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.statistic.metric.ArrayMetric#success
获取窗口内的success个数
1 | public long success() { |
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.statistic.base.LeapArray#currentWindow(long)
1 | public WindowWrap<T> currentWindow(long timeMillis) { |
注释非常详细,需要注意的是resetWindowTo方法,不同子类有不同的实现
- BucketLeapArray:重置窗口开始时间,将各种数据置为0
- OccupiableBucketLeapArray:重置窗口开始时间,将borrowArray中对应时间的MetricBucket的数据作为窗口的数据,而不是直接归零(具体作用在流控中解释)
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.statistic.base.LeapArray#values()
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.statistic.base.LeapArray#values(long)
获取窗口内的所有有效的(非过期)MetricBucket,组成list返回
增加数据(以addSuccess为例)
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.statistic.metric.ArrayMetric#addSuccess
调用currentWindow获取当前窗口后调用value()获取MetricBucket再调用addSuccess(count)方法
滑动窗口类型
分钟级滑动窗口
窗口总长度60秒,每个样本窗口1秒,总共60个样本窗口
private transient Metric rollingCounterInMinute = new ArrayMetric(60, 60 * 1000, false);
秒级滑动窗口
窗口总长度1秒,每个样本窗口500ms,总共2个样本窗口
private transient volatile Metric rollingCounterInSecond =
new ArrayMetric(SampleCountProperty.SAMPLE_COUNT,IntervalProperty.INTERVAL);
PS:秒级窗口不精确,监控中的秒级数据来自于分钟级窗口,只有需要最近1秒的数据时才会使用秒级滑动窗口的值(详情可以看文首第二个链接)
切入流程
(以SpringBoot版本为例)
通过AOP机制织入
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.annotation.aspectj.SentinelResourceAspect
1 |
|
Entry
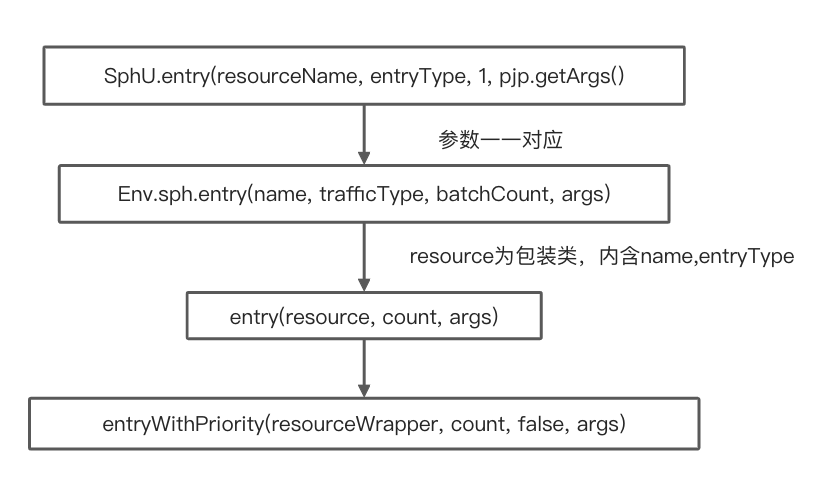
1 | private Entry entryWithPriority(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) |
之后在处理链指针不为空的情况下按序调用进入方法并返回
核心类
Context
Context 代表调用链路上下文,贯穿一次调用链路中的所有 Entry。Context 维持着入口节点(entranceNode)、本次调用链路的 curNode、调用来源(origin)等信息。Context 名称即为调用链路入口名称。
Context 通过 ThreadLocal 传递,只在调用链路的入口处创建。
Context 的字段说明:
- name:Context 的名称。
- entranceNode:当前调用树的入口节点,类型为 EntranceNode。同一个入口的资源,每个资源对应一个 DefaultNode,entranceNode#childList 用于存储这些资源的 DefaultNode。
- curEntry:当前 Entry(CtEntry)。
- origin:调用来源的名称,即服务消费者的名称或者服务消费者的来源 IP,取决于服务消费者是否使用 Sentinel,由 Sentinel 适配层传递过来。例如:服务提供者是 Spring MVC 应用,且服务提供者使用 Sentinel 的 Web MVC 适配,那么 Sentinel 会尝试从请求头获取"S-user",如果服务消费者有在请求头传递这个参数,那么就能够获取到
Entry
在调用 Context#getCurNode 方法获取调用链路上当前访问到的资源的 DefaultNode 时,实际是从 Context#curEntry 获取的,Entry 维护了当前资源的 DefaultNode,以及调用来源的 StatisticNode。
CtEntry 是 Entry 的直接子类
CtEntry 用于维护父子 Entry,每一次调用 SphU#entry 方法都会创建一个 CtEntry。如果服务 B 在处理一个请求的路径上会多次调用 SphU#entry,那么这些 CtEntry 会构成一个双向链表。在每次创建 CtEntry,都会将 Context.curEntry 设置为这个新的 CtEntry,双向链表的作用就是在调用 CtEntry#exit 方法时,能够将 Context.curEntry 还原为上一个资源的 CtEntry。
Node
用于持有实时统计的指标数据
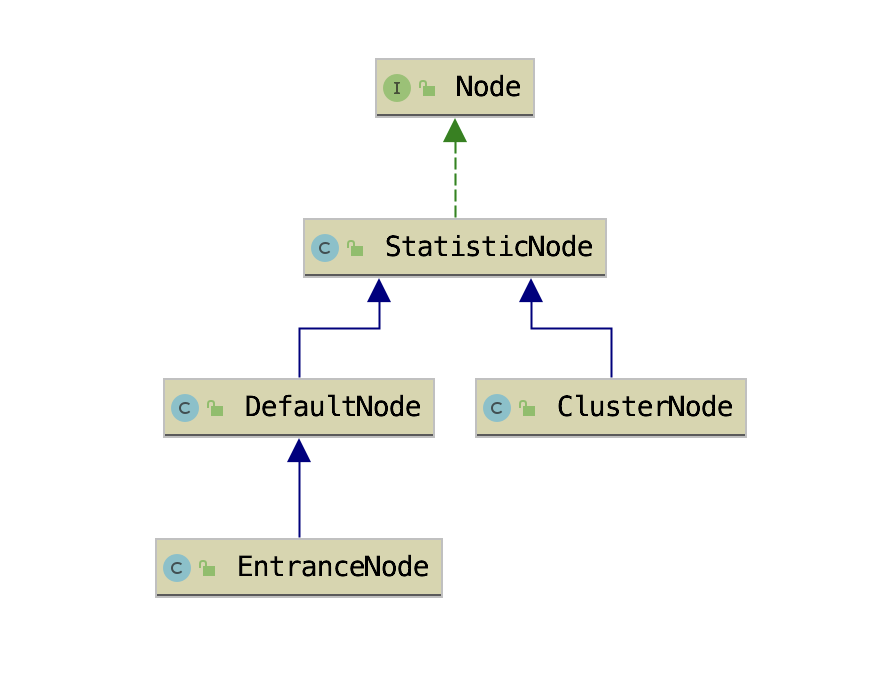
Node实际上是数据节点,主要用于统计各种规则所需要的数据,如QPS,线程数等等。各个Node因为记录数据的不同有以下四个实现
StatisticNode
数据统计节点,核心数据是以下三个
1 | /** |
滑动窗口使用场景
- 获取前一秒被 Sentinel 拒绝的请求总数从分钟级滑动窗口获取
- 获取当前一秒内已经被 Sentinel 拒绝的请求总数则从秒级滑动窗口获取
- 获取最小耗时也是从秒级的滑动窗口获取
StatisticNode 还负责统计并行占用的线程数,用于实现信号量隔离,按资源所能并发占用的最大线程数实现限流。通过控制并发线程数实现信号量隔离的好处就是不让一个接口同时使用完线程池所有线程
数据统计部分采用改进的滑动窗口的方式,时间窗口+Bucket,通过循环复用 Bucket 以减少 Bucket 的创建和销毁。在统计指标数据时,利用当前时间戳定位 Bucket,使用 LongAdder 统计时间窗口内的请求成功数、失败数、总耗时等指标数据优化了并发锁。Sentinel 通过定时任务递增时间戳以获取当前时间戳,避免了每次获取时间戳都使用 System 获取的性能消耗。//todo
DefaultNode
resource * context纬度数据统计节点,存在每个 NodeSelectorSlot 的map里
DefaultNode 字段说明:
- id:资源 ID,ResourceWrapper 对象。
- childList:childList 是一个 Node(DefaultNode)集合,用于存放子节点。
- clusterNode:clusterNode 字段是一个 ClusterNode,ClusterNode 也是 StatisticNode 的子类。
EntranceNode
入口节点,名称相同的 Context 都使用同一个 EntranceNode
ClusterNode
统计每个资源全局的指标数据,以及统计该资源按调用来源区分的指标数据。全局数据指的是不区分调用链路,一个资源 ID 只对应一个 ClusterNode。
ClusterNode 字段说明:
- name:资源名称
- resourceType:资源类型
- originCountMap:维护每个调用来源的指标数据统计数据(StatisticNode)
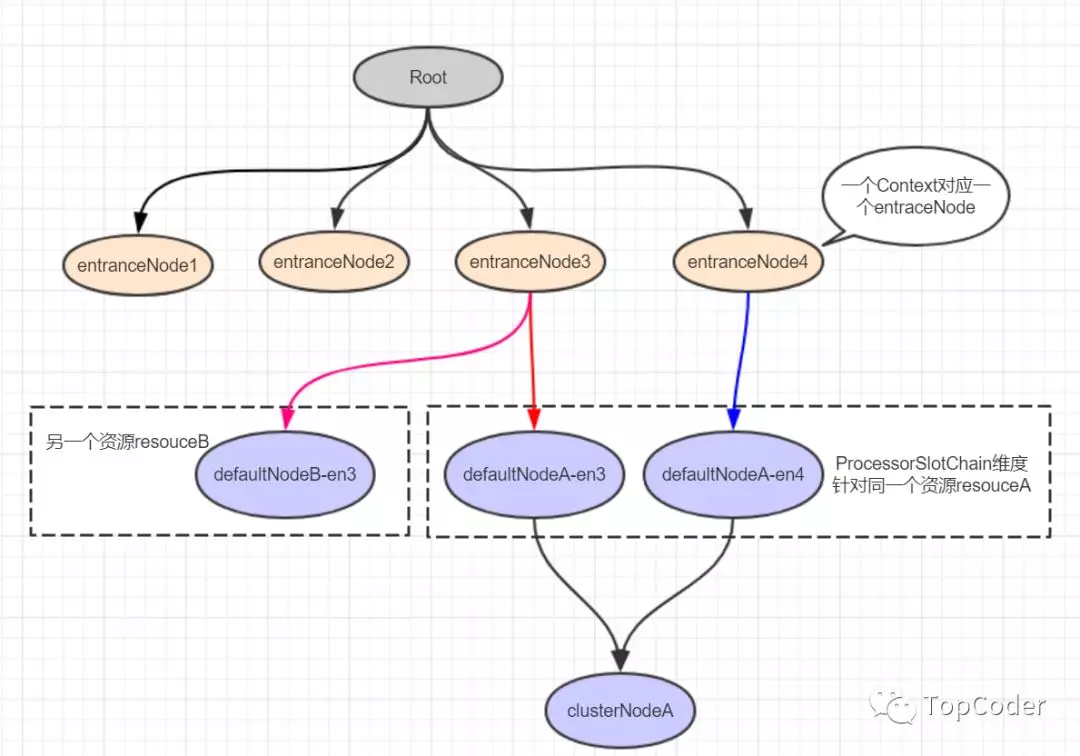
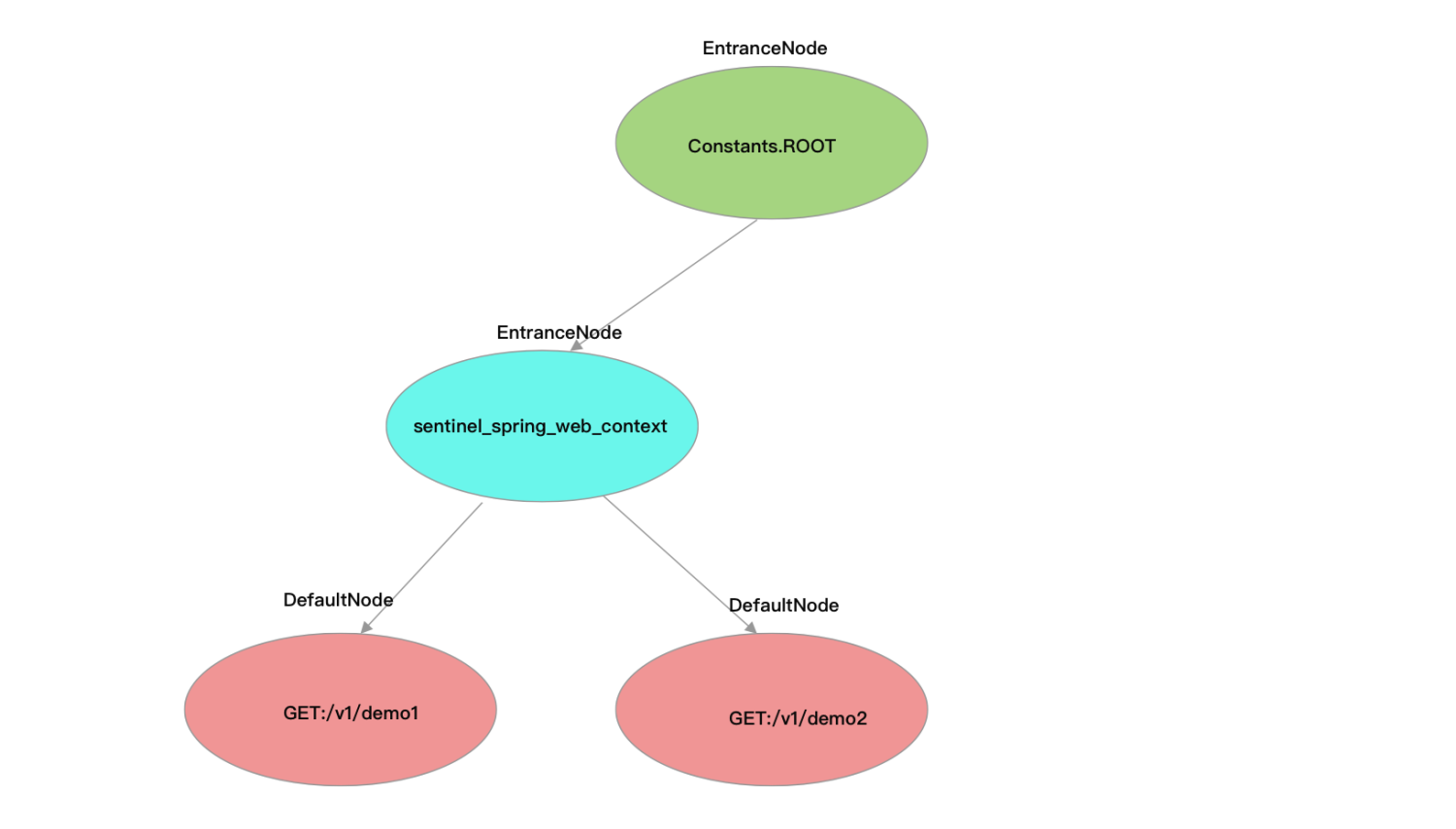
Root与调用树
Constants 常量类用于声明全局静态常量,Constants 有一个 ROOT 静态字段,类型为 EntranceNode。
在调用 ContextUtil#enter 方法时,如果还没有为当前入口创建 EntranceNode,则会为当前入口创建 EntranceNode,将其赋值给 Context.entranceNode,同时也会将这个 EntranceNode 添加到 Constants.ROOT 的子节点(childList)。资源对应的 DefaultNode 则是在 NodeSelectorSlot 中创建,并赋值给 Context.curEntry.curNode。
Constants.ROOT、Context.entranceNode 与 Entry.curNode 三者关系如下图所示。
Slot
处理链上的插槽,核心逻辑所在
整体处理基于责任链模式,通过spi机制按顺序加载处理链,所有ProcessorSlot都继承AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot 类,从而组成单向链表,调用 fireEntry 方法逐个前进或者 fireExit 方法逐个后退
主要分成两类,一类数据统计(NodeSelectorSlot->ClusterBuilderSlot->StatisticSlot(logslot辅助用,暂时放在这类)),一类实现降级以及block
数据统计Slot
NodeSelectorSlot
这个 slot 主要负责收集资源的路径,并将这些资源的调用路径以树状结构存储起来,用于根据调用路径进行流量控制。
- 为当前资源创建 DefaultNode,并且将 DefaultNode 赋值给 Context.curEntry.curNode
- 如果当前调用链路上只出现过一次 SphU#entry 的情况,将该 DefaultNode 添加到的 Context.entranceNode 的子节点,否则添加到 Context.curEntry.parent 的子节点(通过com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.context.Context#getLastNode实现)
1 | private void firstLevel(){ |
ClusterBuilderSlot
这一环的主要作用是构建 ClusterNode,为资源纬度的统计节点
- 如果当前资源未创建 ClusterNode,则为资源创建 ClusterNode;
- 将 ClusterNode 赋值给当前资源的 DefaultNode.clusterNode;
- 如果调用来源(origin)不为空,则为调用来源创建 StatisticNode,用于实现按调用来源统计资源的指标数据,ClusterNode 持有每个调用来源的 StatisticNode。
ps:ClusterBuilderSlot持有非静态private volatile ClusterNode clusterNode = null;,因为一个资源只会创建一个 ProcessorSlotChain,意味着 ClusterBuilderSlot 也只会创建一个,那么让 ClusterBuilderSlot 持有该资源的 ClusterNode 就可以省去每次都从 Map 中获取的步骤
LogSlot
进入时直接fire,在后续节点抛出BlockException后在这里将相关日志记录
StatisticSlot
负责进行数据统计,也是先fire,在后续节点处理完之后,在这里对统计的数据进行记录
entry 方法
请求正常通过
- 当前资源并行占用的线程数增加 1、当前时间窗口被放行的请求总数加 1
- 如果调用来源不为空,也将调用来源的 StatisticNode 的当前并行占用线程数加 1、当前时间窗口被放行的请求数加 1
- 如果流量类型为 IN,则将资源全局唯一的 ClusterNode 的并行占用线程数、当前时间窗口被放行的请求数都增加 1
- 回调所有 ProcessorSlotEntryCallback#onPass 方法
1 | node.increaseThreadNum(); |
捕获PriorityWaitException异常
(特殊情况)
当捕获到 PriorityWaitException 异常时,说明当前请求已经被休眠了一会了,但请求还是允许通过的
- 不需要为 DefaultNode 记录这个请求的指标数据
- 自增当前资源并行占用的线程数
- 为 ClusterNode 自增并行占用的线程数
- 回调所有 ProcessorSlotEntryCallback#onPass 方法
1 | node.increaseThreadNum(); |
捕获到 BlockException 异常
- 将异常记录到调用链路上下文的当前 Entry(StatisticSlot 的 exit 方法会用到)
- 调用 DefaultNode#increaseBlockQps 方法记录当前请求被拒绝
- 将当前时间窗口的 block qps 这项指标数据的值加 1
- 如果调用来源不为空,让调用来源的 StatisticsNode 也记录当前请求被拒绝
- 如果流量类型为 IN,则让用于统计所有资源指标数据的 ClusterNode 也记录当前请求被拒绝
1 | // Blocked, set block exception to current entry. |
捕获到其他异常
- 让 DefaultNode 记录当前请求异常
1 | // Unexpected internal error, set error to current entry. |
exit 方法
由于StatisticSlot 在捕获异常时将异常记录到当前 Entry,exit 方法中通过 Context 可获取到当前 CtEntry,从当前 CtEntry 可获取 entry 方法中写入的异常,从而得知请求的具体状况,完成相应操作
- 计算耗时
- 记录执行耗时与成功总数
- 自减当前资源占用线程数
- 来源不为空,减少来源的线程数
- 流量为In,让用于统计所有资源指标数据的 ClusterNode 也记录相关信息
- 调用回调方法
PS:在 DefaultNode 的相关指标数据收集方法被调用时,ClusterNode 的对应方法也会被调用
限流降级以及流控Slot
AuthoritySlot
权限控制,根据 origin 做黑白名单的控制
SystemSlot
实现自适应限流(针对全局入口流量)
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRuleManager#checkSystem
主要比较参数有successQps,curThreadNum,avgRt,highestSystemLoad,highestCpuUsage
通过起一个后台线程(SystemMetricCollectorTask),每秒查询一次系统负载和CPU使用负载
第一版基于TCP BBR算法(结合自动化控制理论优化中PID controller)
第二版将系统指标(load/CPU usage)作为一个启动条件
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRuleManager#checkSystem
1 | public static void checkSystem(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper) throws BlockException { |
FlowSlot
负责流控功能的实现
由 ProcessorSlot、Checker、Rule、RuleManager 组合完成,ProcessorSlot作为入口,并持有对应的Checker,Checker根据Rule进行检查,RuleManager管理Rule
主要步骤如下
- 在 ProcessorSlot#entry 方法中调用 Checker#check 方法,并将 DefaultNode 传递给 Checker。
- Checker 根据资源名称从 RuleManager 获取为该资源配置的规则。
- Checker 从 传入context,以及node中根据rule和策略获取需要的node
- 如果当前限流规则的 limitApp 不为 default,该限流规则只针对指定调用来源限流。当调用来源与当前限流规则的 limitApp 相等时:
- strategy 为 STRATEGY_DIRECT,则使用调用来源的 StatisticNode,实现针对调用来源限流。
- strategy 为 STRATEGY_RELATE:根据限流规则配置的 refResource 获取引用资源的 ClusterNode,即使用引用资源的指标数据限流。通俗点说就是使用其它资源的指标数据限流,你的并发量高我就限流,让你多处理一点请求,等你并发量降低了,我就不限流了;
- strategy 为 STRATEGY_CHAIN:使用当前资源的 DefauleNode,实现按调用链路的资源指标数据限流。
- 当 limitApp 为 default 时,针对所有来源限流。
- strategy 为 STRATEGY_DIRECT,则使用当前资源的 ClusterNode。
- strategy 为 STRATEGY_RELATE:使用引用资源的 ClusterNode;
- strategy 为 STRATEGY_CHAIN:使用当前资源的 DefauleNode。
- 如果 limitApp 为 other,且该资源的所有限流规则都没有针对当前的调用来源限流。
- 如果 strategy 为 STRATEGY_DIRECT,则使用 origin 的 StatisticNode。
- strategy 为 STRATEGY_RELATE:使用引用资源的 ClusterNode
- strategy 为 STRATEGY_CHAIN:使用当前资源的 DefauleNode
- 如果当前限流规则的 limitApp 不为 default,该限流规则只针对指定调用来源限流。当调用来源与当前限流规则的 limitApp 相等时:
- 根据配置调用对应的controller的canPass方法
- 从node中获取当前时间窗口的某项指标数据(QPS、avgRt 等)与规则的阈值对比,如果达到规则的阈值则抛出 Block 异常。
TrafficShapingController
实现流量塑形的controller主要有以下几种
DefaultController
实现快速失败
1 | public boolean canPass(Node node, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized) { |
RateLimiterController
实现排队等待
设置 QPS 为 10,那么每 100 毫秒允许通过一个,通过计算当前时间是否已经过了上一个请求的通过时间 latestPassedTime 之后的 100 毫秒,来判断是否可以通过。假设才过了 50ms,那么需要当前线程再 sleep 50ms,然后才可以通过。如果同时有另一个请求呢?那需要 sleep 150ms 才行。
1 | public boolean canPass(Node node, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized) { |
WarmUpController
实现Warm Up
Warm Up,冷启动。在应用升级重启时或长时间低压力之后,应用自身需要一个预热的过程,预热之后才能到达一个稳定的性能状态,比如说,接口预热阶段完成 JIT 即时编译、完成一些单例对象的创建、线程池的创建、各种连接池的初始化、或者执行首次需要加锁执行的代码块。核心算法借鉴了Guava中SmoothWarmingUp的实现,详细分析见
https://www.javadoop.com/post/rate-limiter
https://www.jianshu.com/p/280bf2dbd6f0(推荐这篇)
在构造函数中通过double count, int warmUpPeriodInSec, int coldFactor三个参数,计算出warningToken,maxToken,slope
但是由于关注的qps所以对一些变量进行了替换
- warmupPeriod=warmUpPeriodInSec
- stableInterval=1/count
- maxPermits=maxToken
- thresholdPermits=warningToken
1 | private void construct(double count, int warmUpPeriodInSec, int coldFactor) { |
通过判断计算该点对应的qps阈值,进行判断
1 | public boolean canPass(Node node, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized) { |
1 | protected void syncToken(long passQps) { |
WarmUpRateLimiterController
RateLimiterController与WarmUpController的结合
通过WarmUpController中一样的算法计算出当前的qps阈值,再用该阈值去计算等待时间
DegradeSlot
实现熔断降级的切入点,功能由ProcessorSlot、CircuitBreaker、DegradeRule、DegradeRuleManager组合完成。且经过一次升级,通过状态间的自动转换避免了原版本使用定时器的缺点。
熔断策略
- SLOW_REQUEST_RATIO:按慢请求比率
- ERROR_RATIO:按失败比率
- ERROR_COUNT:按失败次数
ExceptionCircuitBreaker实现根据异常比例熔断
ResponseTimeCircuitBreaker实现根据RT时间熔断
slot中通过调用两者的onRequestComplete方法统计并且判断是否熔断的逻辑
熔断器状态
- 当熔断器状态为半开启状态时,直接拒绝请求;
- 当熔断器为关闭状态时,请求被允许通过;
- 当熔断器状态为开启状态时,根据 timeWindow 尝试将开关状态改为半闭合,如何修改成功,则允许当前请求通过。
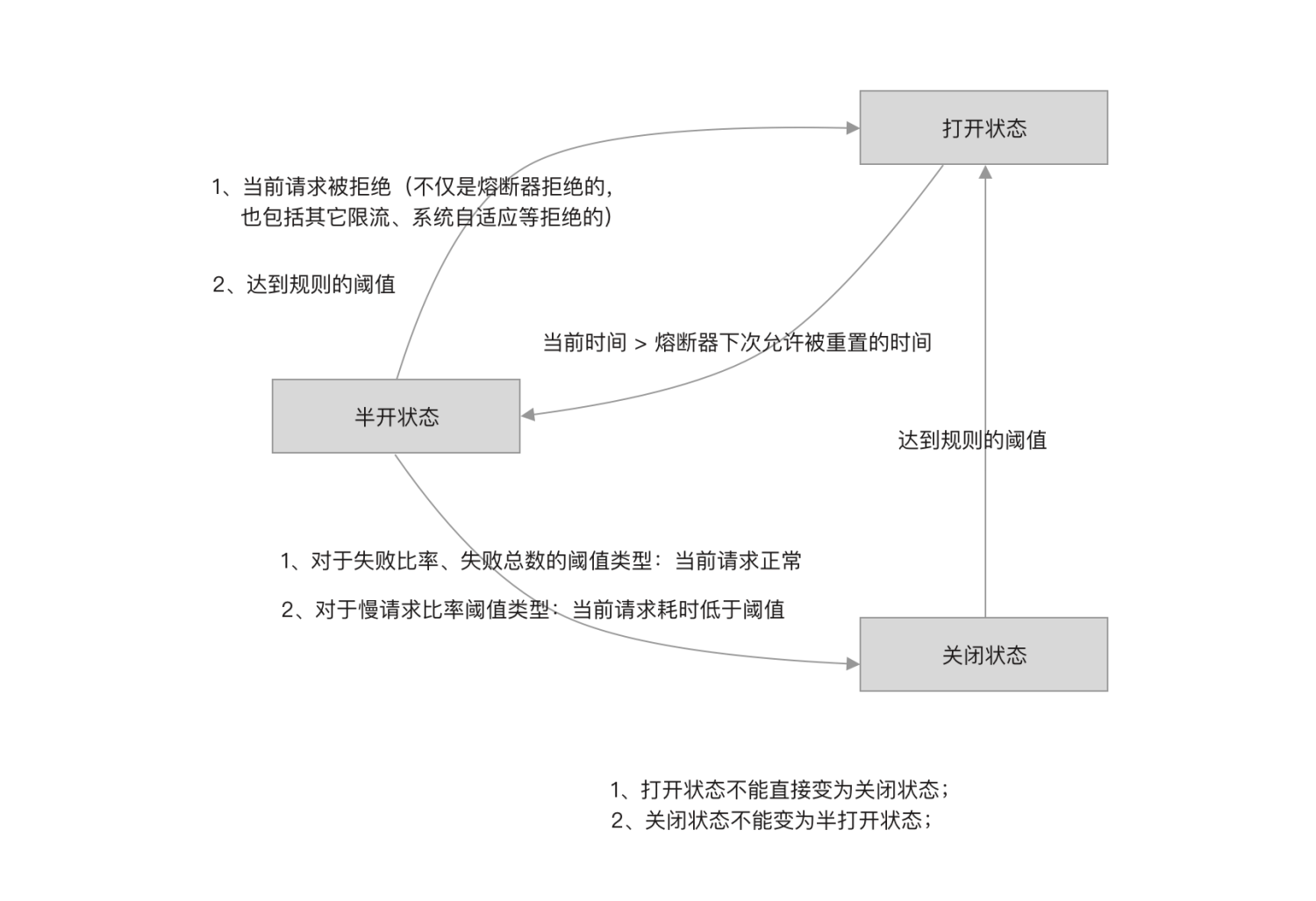
详细分析
这一块的实现,内部版本与开源版本略有不同,这边的分析以开源版本为例。
核心方法如下
AbstractCircuitBreaker#tryPass
1 | public boolean tryPass(Context context) { |
AbstractCircuitBreaker#状态转换
基本都是使用CAS机制更改状态并且调用监听
下面展示的是解决一个bug的临时方案
1 | protected boolean fromOpenToHalfOpen(Context context) { |
ExceptionCircuitBreaker#onRequestComplete
1 | public void onRequestComplete(Context context) { |
ResponseTimeCircuitBreaker#onRequestComplete
整体类似上一个方法,不再赘述
一些对应关系
一个context(context name为唯一标识,context跟着线程走,切换线程需要手动切换)
- 对应 一个调用链路 (默认值为sentinel_default_context)
- 对应一个 entrancenode(在Context.enter时创建)
一个resource (resource name为唯一标识)
- 对应一个责任链实例(共享同一个 NodeSelectorSlot 实例以及 ClusterBuilderSlot实例)
- 对应一个ClusterNode(不同origin会在该ClusterNode下挂不同的数据节点)
一个DefaultNode(维持调用树状结构)
- 对应一个context下的一个resource,即它的纬度是context*resource,存在NodeSelectorSlot的map中(key为context name)

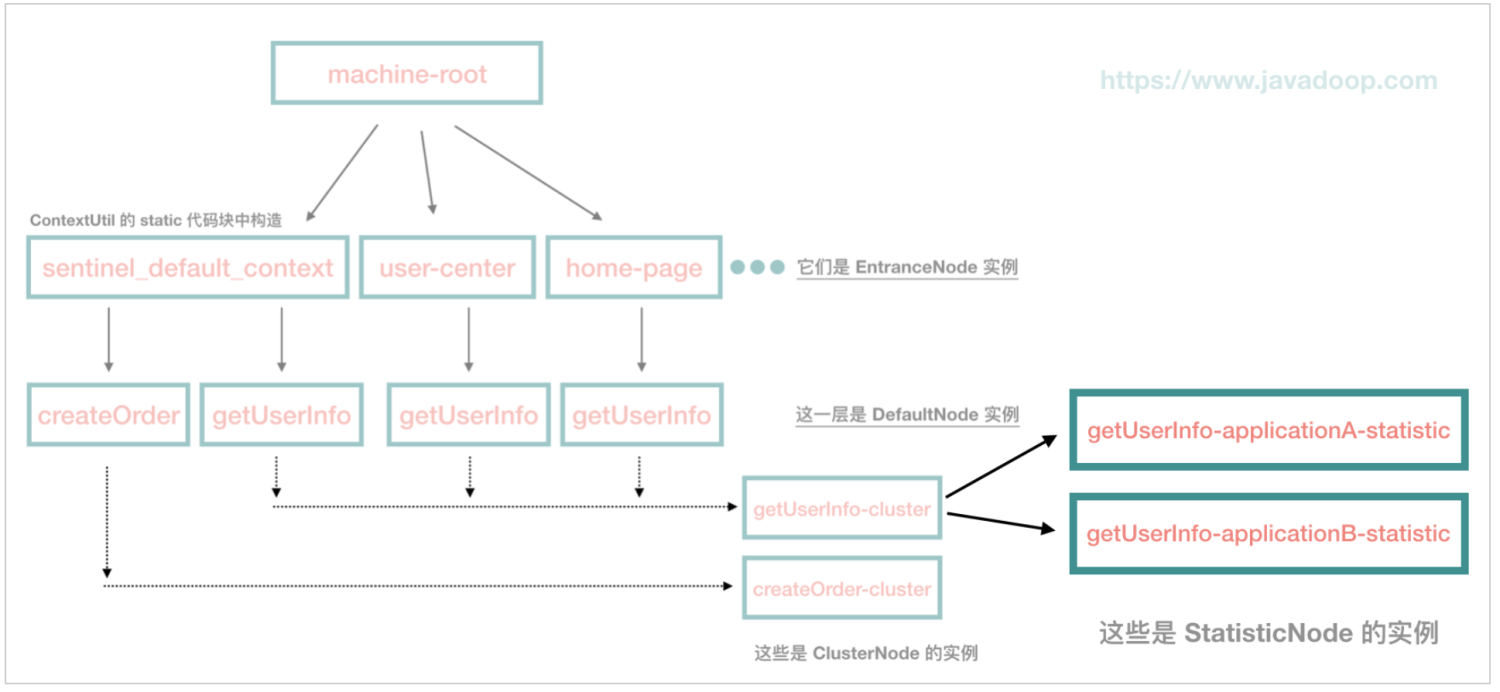
举例
1 | //规则 |
1 | public class App |
参考链接
https://github.com/sentinel-group/sentinel-awesome