简介
由于流量存在不均匀的情况,单机限流无法实现准确的集群限流,往往在总流量没有到达集群阈值的情况下,集群中的某些机器就开始限流。例如一个集群限流阈值为200qps,由两个节点组成,那么每个节点限流配置100qps,在这种配置下即便集群流量未到达200qps,单个节点也有可能到达100qps而开始限流。而集群限流就是为这种场景服务的,目的就是实现精确地控制整个集群的 QPS。
模块简介
sentinel-cluster-common-default:公共模块,定义通信协议,包括编码器和解码器接口、请求和响应实体(数据包),与底层使用哪种通信框架无关
sentinel-cluster-client-default:集群限流客户端模块,实现公共模块定义的接口,使用 Netty 进行通信,实现自动连接与掉线重连、提供连接配置 API
sentinel-cluster-server-default:集群限流服务端模块,实现公共模块定义的接口,使用 Netty 进行通信,同时提供扩展接口对接规则判断的具体实现(TokenService)
sentinel-cluster-server-envoy-rls:提供了Envoy 集群流量控制,使sentinel具有在Service Mesh下的流控能力
核心原理
单机限流流程
- FlowSlot 作为切入点,在 entry 方法中调用 FlowRuleChecker#checkFlow 方法判断是否限流;
- FlowRuleChecker 根据资源名称从规则管理器获取配置的限流规则,遍历限流规则;
- 根据限流规则的 clusterMode 决定走本地限流逻辑还是走集群限流逻辑;
- 如果是本地限流,则调用流量效果控制器判断是否拒绝当前请求。
由于网络延迟的存在,Sentinel 集群限流并未实现匀速排队流量效果控制,也没有支持冷启动,而只支持直接拒绝请求的流控效果。(具有优先级的流量在一定情况下可以尝试抢占之后的时间窗口的指标,见core部分DefaultController)
集群限流流程
在上述第(3)步中如判断为集群限流,则通过远程调用向集群限流服务端(TokenService)发起调用,由TokenService判断是否拒绝请求。结合令牌桶的思想,TokenService类似于令牌发放员,负责生产令牌,客户端向服务端申请令牌。
服务模式
Sentinel 集群限流客户端与集群限流服务端通信只保持一个长连接,底层通信基于 Netty 框架实现,自定义通信协议,并且数据包较小,网络 I/O 性能方面影响不大。
Sentinel 集群限流对限流服务端的可用性要求不高,当限流服务端挂掉时,可回退为本地限流。
嵌入模式
简单理解为,TokenService作为应用的内置服务同应用一起启动,可动态挑选一个节点作为TokenService(不具备类似主从自动切换的功能)
独立模式
单独部署的TokenService,可以为多个服务提供集群限流支持
整体扩展架构
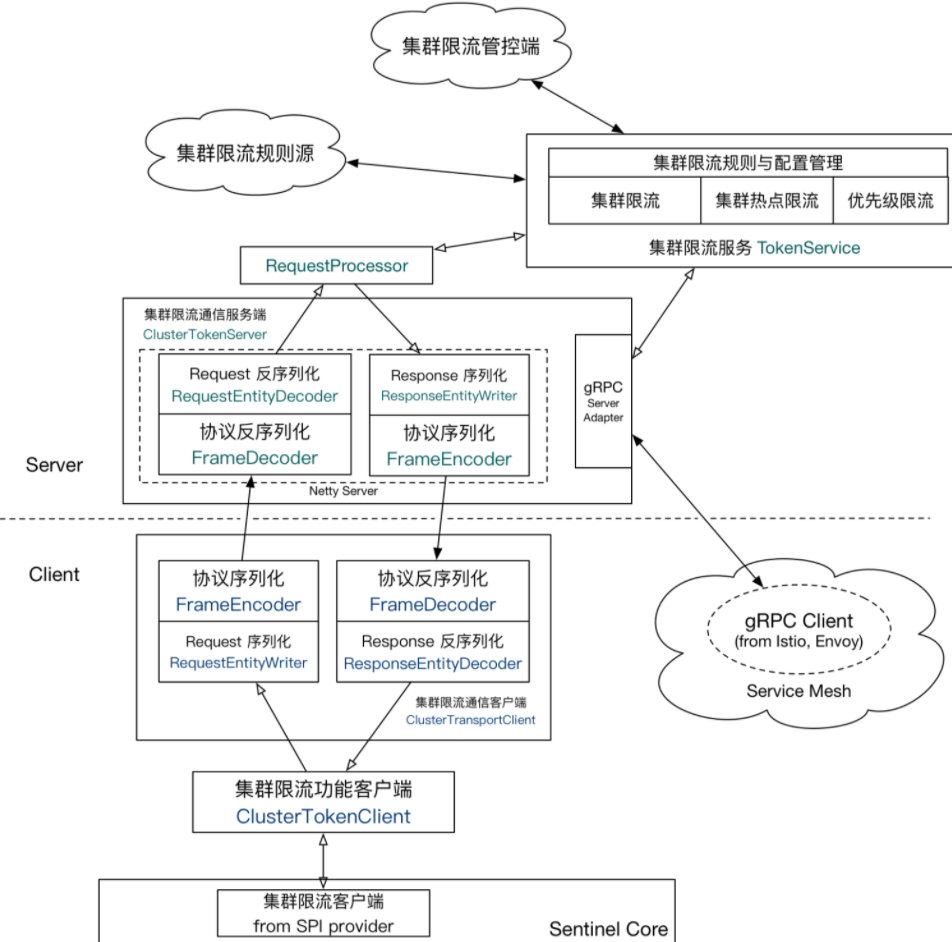
核心类及流程
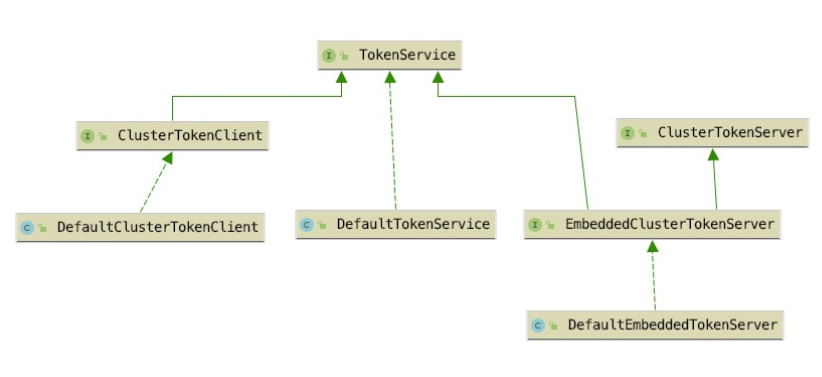
sentinel-core 模块的 cluster 包
定义了实现集群限流功能的相关接口
- TokenService:定义客户端向服务端申请 token 的接口,由 FlowRuleChecker 调用
- ClusterTokenClient:集群限流客户端需要实现的接口,继承 TokenService
- ClusterTokenServer:集群限流服务端需要实现的接口
- EmbeddedClusterTokenServer:支持嵌入模式的集群限流服务端需要实现的接口,继承 TokenService、ClusterTokenServer
在上图中DefaultClusterTokenClient是 sentinel-cluster-client-default 模块中的 ClusterTokenClient 接口实现类,DefaultTokenService 与 DefaultEmbeddedTokenServer 分别是 sentinel-cluster-server-default 模块中的 ClusterTokenServer 接口与 EmbeddedClusterTokenServer 接口的实现类。
当使用嵌入模式启用集群限流服务端时,使用的是 EmbeddedClusterTokenServer,否则使用 ClusterTokenServer,通过 Java SPI 实现
集群限流客户端
与单机限流的不同之处从FlowRuleChecker#canPassCheck开始,在该方法中若判断为集群限流则调用FlowRuleChecker#passClusterCheck方法
FlowRuleChecker#passClusterCheck(……)
1 | private static boolean passClusterCheck(FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node, int acquireCount, |
pickClusterService()
如果当前节点是客户端角色,获取ClusterTokenClient实例;如果当前节点是服务端角色(嵌入式),获取EmbeddedClusterTokenServer实例
requestToken(flowId, acquireCount, prioritized)
1 | public TokenResult requestToken(Long flowId, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized) { |
applyTokenResult(result, rule, context, node, acquireCount, prioritized)
- 当响应状态码为 OK 时放行请求;
- 当响应状态码为 SHOULD_WAIT 时,休眠指定时间再放行请求;
- 当响应状态码为 BLOCKED,直接拒绝请求;
- 其它状态码均代表调用失败,根据规则配置的 fallbackToLocalWhenFail 是否为 true,决定是否回退为本地限流,如果需要回退为本地限流模式,则调用 passLocalCheck 方法重新判断。
集群限流服务端
从客户端发来的requestToken请求最后交由com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.cluster.flow.DefaultTokenService#requestToken方法处理
DefaultTokenService#requestToken(Long ruleId, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized)
1 | public TokenResult requestToken(Long ruleId, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized) { |
ClusterParamFlowChecker#acquireClusterToken
1 | static TokenResult acquireClusterToken(/*@Valid*/ FlowRule rule, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized) { |
ClusterParamFlowChecker#calcGlobalThreshold
1 | private static double calcGlobalThreshold(ParamFlowRule rule, Object value) { |
ClusterMetric#tryOccupyNext
简化版的DefaultControlle,只尝试占用下一个样本窗口的指标
1 | public int tryOccupyNext(ClusterFlowEvent event, int acquireCount, double threshold) { |
滑动窗口
集群限流使用的滑动窗口并非 sentinel-core 模块下实现的滑动窗口,而是 sentinel-cluster-server-default 模块自己实现的滑动窗口
实现集群限流需要收集的指标数据有以下几种:
1 | public enum ClusterFlowEvent { |
- PASS:已经发放的令牌总数
- BLOCK:令牌申请被驳回的总数
- PASS_REQUEST:被放行的请求总数
- BLOCK_REQUEST:被拒绝的请求总数
- OCCUPIED_PASS:预占用,已经发放的令牌总数
- OCCUPIED_BLOCK:预占用,令牌申请被驳回的总数
- WAITING:当前等待下一个时间窗口到来的请求总数
除统计的指标项与 sentinel-core 包下实现的滑动窗口统计的指标项有些区别外,实现方式都一致。
总结
集群限流并非解决请求倾斜问题,在请求倾斜严重的情况下,集群限流可能会导致某些节点的流量过高,导致系统的负载过高,这时就需要使用系统自适应限流、熔断降级作为兜底解决方案。
参考资料
https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E9%9B%86%E7%BE%A4%E6%B5%81%E6%8E%A7